2025-06-05
Glucose Control Systems with PID Control and AI Prediction Abstract:
This project aims to develop an integrated approach to control and predict blood glucose levels in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) by combining an insulin delivery method with advanced artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms. The project consists of two main parts: (1) the implementation of an insulin delivery system using a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controller, and (2) the utilization of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data and AI algorithms for predicting future blood glucose levels, a capability beyond the scope of the PID controller. This combined system offers personalized treatment and with prediction capability it can give early warning to medical staff to manage T1D patients more effectively.
Introduction:
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic condition characterized by insufficient insulin production, leading to unstable blood glucose levels. Maintaining optimal blood glucose control is crucial for T1D patients to prevent complications and ensure a
healthy lifestyle. This project aims to address this challenge by integrating an insulin delivery method and AI-based glucose level prediction.
Insulin Delivery System with PID Control:
In the first part of the project, an innovative insulin delivery system is introduced. A virtual patient model is employed to simulate real patients’ blood glucose levels. The system utilizes a PID controller to regulate the amount of insulin delivered and achieve optimal blood glucose control. The PID controller is carefully tuned to prioritize the prevention of low blood glucose levels (hypoglycemia) while maintaining a balance to avoid high glucose levels (hyperglycemia), ensuring patient safety.
The following graphs show the main concept and result of the first part of the project. 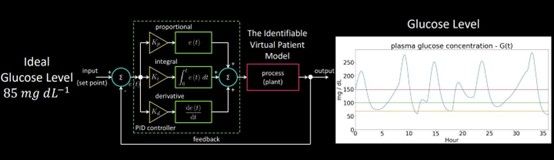
AI Prediction Model with CGM Data:
The second part of the project focuses on leveraging CGM data and advanced AI algorithms to predict patients’ future blood glucose levels. By using continuous and extensive data provided by CGM, a recurrent neural network (RNN) model is trained to offer alternative predictions and personalized treatment plans for T1D patients. To mitigate the impact of error accumulation over time, the AI model is designed to predict glucose levels within a specific near-future timeframe of approximately 5 to 15 minutes. This narrower prediction window enhances accuracy and reliability, enabling healthcare professionals to make timely interventions and adjustments.
The following graphs show the main concept and result of the second part of the project. 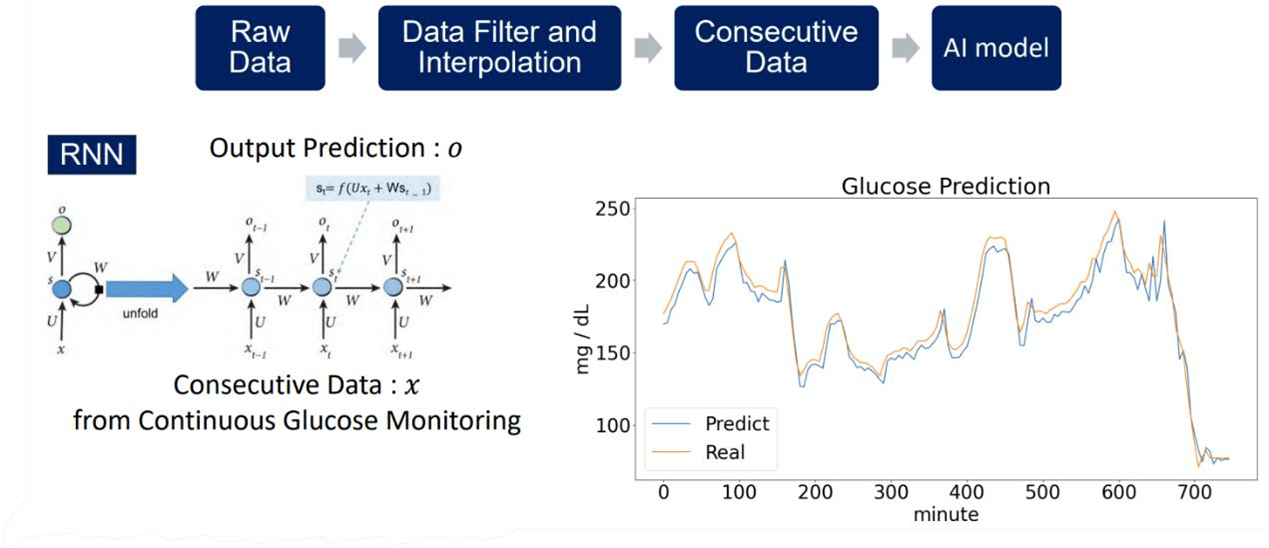
Advantages and Implications:
The combination of the insulin delivery system with PID control and the AI prediction model provides several significant advantages. Firstly, it facilitates personalized treatment by considering individual variations in insulin requirements and metabolic responses. This approach ensures better glucose control to each patient’s specific needs. Secondly, the system offers early warning signs of high and low blood glucose episodes, enabling medical staff to intervene promptly and prevent potential complications.
Conclusion:
The Glucose Control Systems with PID Control and AI Prediction project presents an integrated approach to manage blood glucose levels in patients with T1D. By combining an insulin delivery system with PID control and AI prediction using CGM data, the project offers personalized treatment and early warning capabilities, ultimately contributing to improved glucose control and enhanced patient well-being.


EDPS Systems Limited EDPS 電腦系統有限公司 EA Licence No. 78592
© Copyright of EDPS Systems Limited 2026. All Rights Reserved.